Empower and streamline
governance workflows
CGBOD helps organizations automate audits, manage risks, and maintain ISO compliance — all in one smart, secure, and scalable platform.
Trusted by fast growing startups








How it works
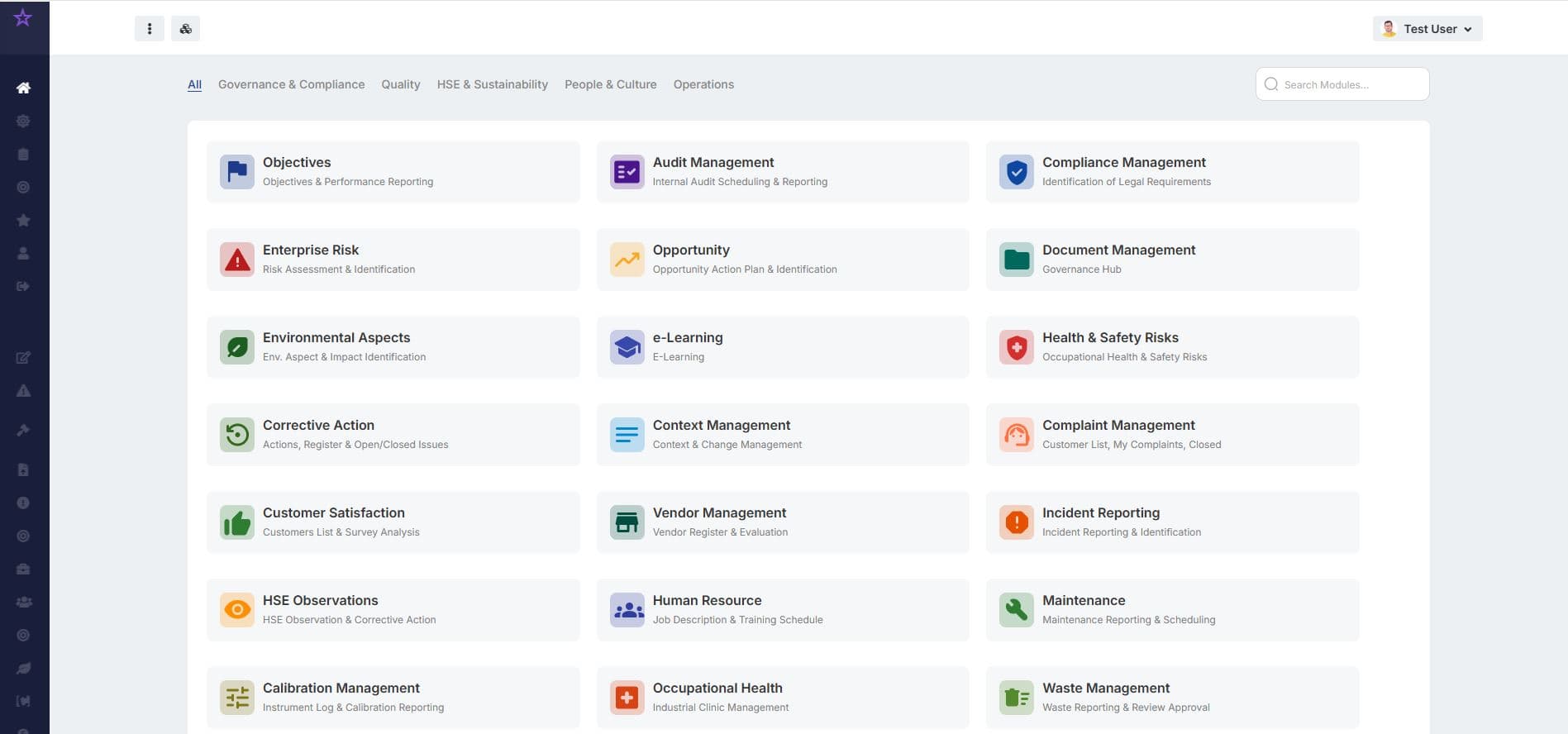
Integrates seamlessly
CGBOD connects your audit, risk, document, and compliance modules into one smart governance ecosystem — enabling efficiency, visibility, and control across your management system.
Configure Your System
Set up modules for Audit, Risk, Document, and HSE management — aligned with ISO 9001, ISO 14001, and ISO 45001 requirements.
Connect Your Teams
Enable real-time collaboration across departments — from Quality and EHS to Management Review teams.
Deploy & Monitor
Launch your digital management system, track performance, and review KPIs through dashboards and analytics.
QMS Internal Audit – Plant 3
Features
Built for Intelligent Workflows
Streamline compliance, audits, and risk management with a visual interface designed for operational teams.
Agent Activity Tracker
Monitor agent workflows with detailed logs, including triggers, tools used, outcomes, and timestamps — all in one place.

Workflow & Compliance Builder
Design, preview, and deploy workflows visually. Simplify audit trails, risk management, and ISO compliance tasks.
Use Cases
Empowering Teams Across Operations
CGBOD enables compliance, audit, and operations teams to maintain full control, visibility, and accountability across departments.
Governance & Risk
Monitor organizational governance and mitigate risks through real-time visibility and automated alerts.
Compliance Management
Map and manage ISO, GDPR, and SOC 2 requirements effortlessly with centralized documentation control.
Incident & Audit
Track, report, and resolve non-conformities or audit findings using structured, role-based workflows.
HR & Training
Assign mandatory policy training, track acknowledgments, and maintain skill and compliance records.
Performance & KPIs
Define, monitor, and report compliance KPIs across departments with dynamic dashboards.
Data & Access Control
Ensure secure document storage, version control, and permission-based access for sensitive data.
It's like adding 15 full-time employees
CGBOD automates repetitive compliance and governance work — from audit prep to document control — freeing teams to focus on actual decision-making instead of paperwork. It's the same output as adding a full department, without increasing headcount.
COMPLIANCE ROI
312%
Enterprises achieved up to 312% ROI by automating audits, risk assessments, and policy tracking through CGBOD.
MANUAL HOURS SAVED
68,000+
Teams cut down more than 68,000 manual hours annually by eliminating repetitive reporting and Excel-based tracking.
AUDIT EFFICIENCY
4x Faster
Internal and external audits now complete up to four times faster with centralized evidence and automated workflows.
PAYBACK PERIOD
<5mo
Most organizations reached full payback within five months of implementation — measurable ROI, real outcomes.
*Based on time-efficiency benchmarks and productivity gains from CGBOD enterprise clients. View performance report
Pricing
Simple and Feasible Pricing
Choose the right plan for your team and scale as you grow
- Includes 5 users
- All features of the module
- Cloud hosting & backups
- Support included
- Module updates
- $150/ 5-user pack / Module/ year
- No per-user billing
- Add users in bundles of 5
- Scales easily as your team grows
- Unlimited data storage
- Alerts and notifications
Module Bundles
Fast moving startups
- All features of the module
- Cloud hosting & backups
- Support included
- Module Updates
- No per-user billing
- Scales easily as your team grows
- Unlimited data storage
- Alerts and notifications
- Includes 50 users
- $125/ 20-user pack / Module/ year
- Add users in bundles of 20
- All features of the module
- Cloud hosting & backups
- Support included
- Module Updates
- No per-user billing
- Unlimited data storage
- Alerts and notifications
- New released modules
- Priority support
- Custom workflows
- API & integration support
For security first teams
Scale securely with confidence
Our AI assistant is designed with enterprise-grade security practices and is compliant with global data protection standards.
CCPA
GDPR
ISO 27001
FAQs
Frequently Asked Questions
Find all your doubts and questions in one place. Still couldn't find what you're looking for?
Seamless Integrations
Connect with your favorite tools and services. Our platform integrates with over 100+ applications to streamline your workflow and boost productivity.